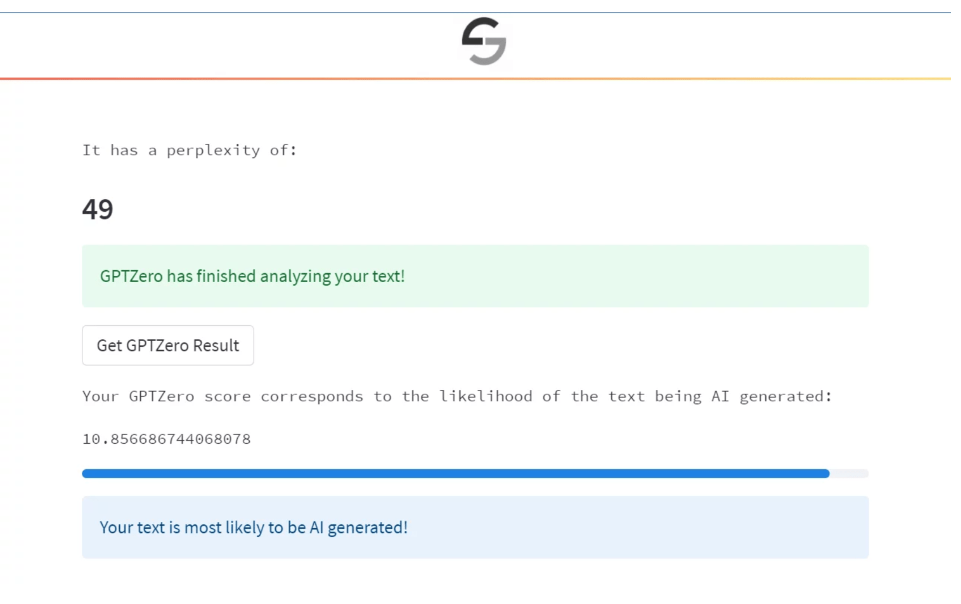
Edward Tian, a computer science major with a journalism minor, created the programme GPTZero. It is made to recognise essays written by the ChatGPT language model, which is powered by AI, in order to determine whether an essay was written by a human or an AI.
GPTZero was developed by Tian during his winter break in order to address the expanding problem of AI plagiarism. There have been cases of students turning in AI-generated assignments as their own since ChatGPT’s launch in late November. Tian’s efforts are not the only ones being made in the war against AI plagiarism. The company that created ChatGPT, OpenAI, is exploring ways to watermark GPT-generated text with a “unnoticeable secret signal” that will allow its source to be identified. Hugging Face released a tool that recognises text produced by GPT-2, an earlier version of the model, demonstrating the open-source community’s commitment to preventing malicious uses of AI. These tools are being used by educators as well, such as a philosophy professor in South Carolina, to detect plagiarism in student work. The creation and use of GPTZero shows a rising awareness of AI plagiarism and a concerted effort to address it.
It would be advantageous for educators, professors, and academic institutions to ensure that submitted assignments are original and not produced by AI because the tool is designed to detect essays written by ChatGPT. Publishers, editors, or anyone else involved in ensuring the legitimacy and originality of written content might also find it interesting.
>>> We invite you to use the latest ChatGPT Demo Free in 2024
DEMO
Similar Apps
Openai AI Text Classifier

GPT Minus1

GPT 2 Output Detector

Chatgpt GPT3 Content Detector

AI Content Detector